A Quick Guide to Common Stock: Definitions, Formulas, Examples, and Differences from Capital Stock
The capital raised through this method is used to finance the working of the business. Common stockholders have voting rights and are entitled to get dividend on their holdings. Many companies pay dividends to their shareholders, providing a regular income stream in addition to potential capital gains. The par value of a share of stock is sometimes defined as the legal capital of a corporation. However, some states allow corporations to issue shares with no par value. If a state requires a par value, the value of common stock is usually an insignificant amount that was required by state laws many years ago.
- NerdWallet, Inc. does not offer advisory or brokerage services, nor does it recommend or advise investors to buy or sell particular stocks, securities or other investments.
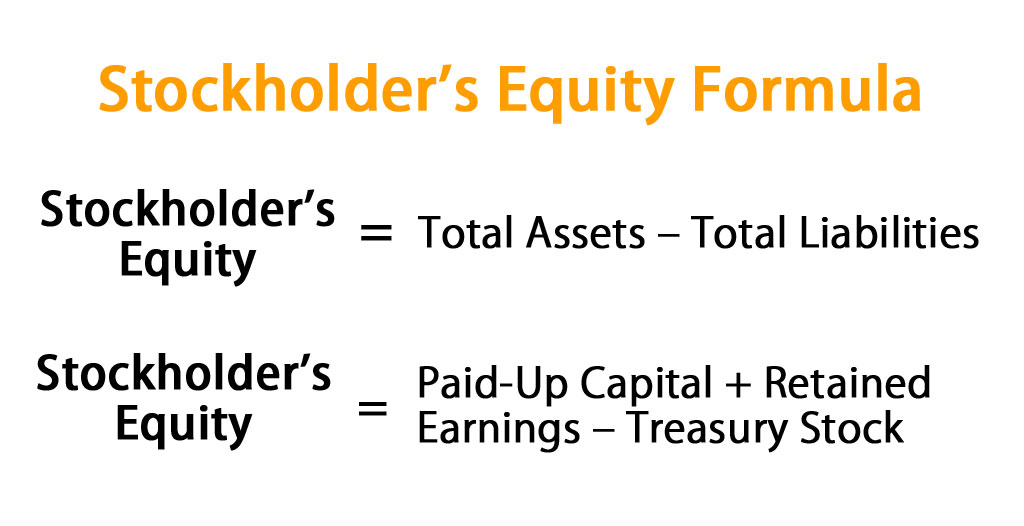
- You can calculate this by subtracting the total assets from the total liabilities.
- It is calculated either as a firm’s total assets less its total liabilities or alternatively as the sum of share capital and retained earnings less treasury shares.
- Research the companies you’re interested in and get to know their business models, financial health, and growth prospects.
- In bankruptcy, common stockholders are last in line for claims, which could result in the loss of the entire investment.
Is Stockholders’ Equity Equal to Cash on Hand?
Stockholders‘ equity might include common stock, paid-in capital, retained earnings, and treasury stock. A preferred stock does not come with any voting rights but does come with more monetary benefits than common stocks. For example, preferred stock shareholders receive dividends on their investment before any common stock shareholders. The issuance of common stock cannot be more than the authorized number but can give less than the number of authorized shares. For example, the company issued 2000 shares during a public offering. So, in this case, the number of shares issued is equal to the company’s outstanding shares.
How Do I Use Common Stock to Vote at Company Meetings?
Smaller companies that can’t meet the listing requirements of these major exchanges are considered unlisted and their stocks are traded over the counter. The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice. All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly.
Pros and Cons of Preferred Stock
Common stocks, however, have the potential to outpace inflation by providing returns that exceed the rate of inflation. This makes them a valuable tool for preserving and growing wealth in the long run. Common stocks are highly liquid assets, meaning they can be bought and sold quickly on the stock market. This liquidity gives you flexibility, allowing you to easily adjust your portfolio in response to market conditions or changes in your investment goals. Common stocks are highly liquid, meaning they can be easily bought and sold on stock exchanges.
Get stock recommendations, portfolio guidance, and more from The Motley Fool’s premium services. Stockholders‘ equity is also referred to as shareholders‘ or owners‘ equity. Current liabilities are debts typically due for repayment within one year, including accounts payable and taxes payable. Long-term liabilities are obligations that are due for repayment in periods longer than one year, such as bonds payable, leases, and pension obligations. Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance.
Book Value of Equity vs. Market Value of Equity: What is the Difference?
They can either be company promoters, insiders, or outside investors. If your stocks pay dividends, consider reinvesting them to buy more shares. This can help you grow your investment over time without having to put in additional money.
Common stockholders may run the risk of losing their entire equity in a company because they are paid out last, after bondholders and preferred stockholders. For investors, common stock enables them to invest in securities that appreciate without significant effort on their part.Common stock dividends can also become an important source of income. Class A shares are available via the GOOGL ticker and come with voting rights. Class C shares are available via the GOOG ticker and do not carry voting rights. In some cases, the balance sheet may also show more information about the common stock, such as how many shares are still outstanding and how much they were sold for.
In addition to financial benefits, owning common stock often grants voting rights, allowing shareholders to influence important corporate decisions. The constant-growth model is a way to value a stock by assuming that the growth rate remains constant. This means that the present value of the stock equals the sum of all future investor dividends, paid out over an indefinite time period. While this model may seem oversimplified, it can provide a useful starting point for the valuation.
These earnings, reported as part of the income statement, accumulate and grow larger over time. At some point, accumulated retained earnings may exceed the amount of contributed equity capital and can eventually grow to be the main source of stockholders‘ equity. Investing directly in individual stocks can take a little more work — and entails a little more risk — but also has the potential to yield much higher returns than index funds. Make sure to research stocks thoroughly before buying them to make sure you understand the potential upsides and downsides of the investment.
By comparing total equity to total assets belonging to a company, the shareholders equity ratio is thus a measure of the proportion of a company’s asset base financed via equity. After the repurchase of the shares, ownership of the company’s equity returns to the issuer, which reduces the total outstanding share count (and net dilution). For mature companies consistently profitable, the retained earnings line item can contribute the highest percentage of shareholders’ equity. In these types of scenarios, the management team’s decision to add more to its cash reserves causes its cash balance to accumulate.
Unlike common stock, preferred stock is not accompanied by voting rights and fixed dividends. To locate common stock on a balance sheet, look under the “Stockholders’ Equity” section. Here, you’ll often find plain english accounting common stock listed with its par value and sometimes additional information, such as the number of issued shares. If not detailed there, notes accompanying the financial statements may hold further insights.