Standard Costs and Variance Analysis Principles of Managerial Accounting
Standard costing is an area within management and cost accounting that relates to establishing standards. For most companies, establishing and controlling costs is a significant factor in increasing profitability. However, these companies cannot manage their costs if they don’t have a benchmark against which to check. Therefore, standard costing helps companies in establishing those benchmarks.
Financial and Managerial Accounting
During the period, Brad projected he should pay $675,000 for direct labor to produce 150,000 units. The total direct labor variance can be calculated in the last line of the top section by subtracting the actual amounts from the standard amounts. The standard quantity allowed of 37,500 direct labor hours less the actual hours worked of 45,000 hours yields a variance of (7,500) direct labor hours.
Direct Labor Variance
- By so doing, the full $719,000 actually spent is fully accounted for in the records of Blue Rail.
- The total direct labor variance was favorable $8,600 ($183,600 vs. $175,000).
- In the last section, we learned how variance analysis helps businesses.
- The standard and actual amounts for direct materials quantities, prices, and totals are calculated in the top section of the direct materials variance template.
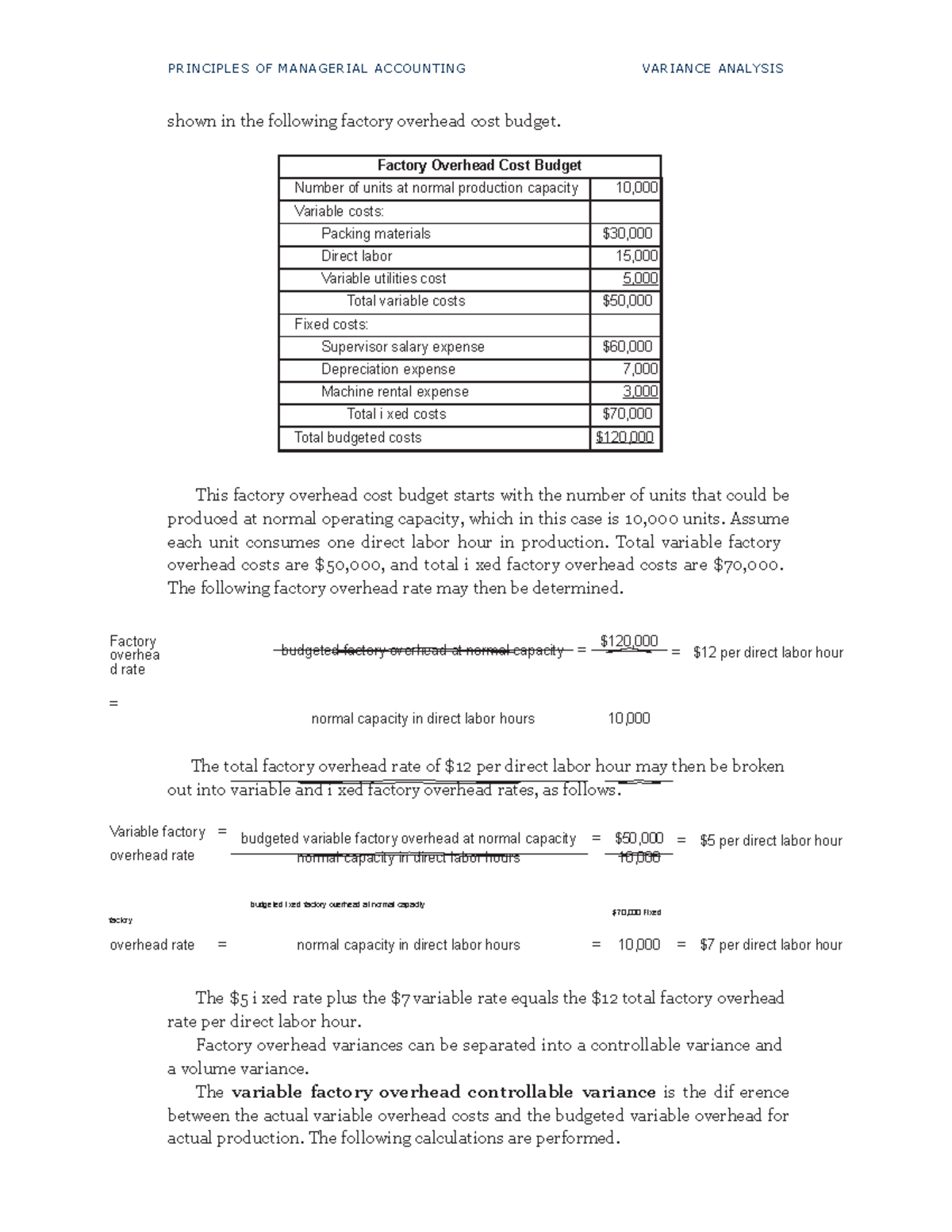
- At the highest level, standard costs variance analysis compares the standard costs and quantities projected with the amounts actually incurred.
Per the standard cost formulas, Brad projected he should have paid $315,000 for the direct materials necessary to produce 150,000 units. To illustrate standard costs variance analysis for variable manufacturing overhead, refer to the data for NoTuggins in Exhibit 8-1 above. Variable manufacturing overhead is applied based on direct labor hours. Per the standards, the variable manufacturing overhead rate is $3 and each unit requires 0.25 direct labor hours.
Practice Video Problem 8-2: Computing direct labor variances LO3

As demonstrated in this chapter, standard costs and variance analysis are tools used to project manufacturing product costs and evaluate production performance. Standard costs variance analysis is used to determine the variances between the standard amounts projected for manufacturing costs and the actual amounts incurred. Any variance between the standard amounts allowed and actual amounts incurred should be investigated.
The profit variance is unfavorable because they fell short of their target profit by $1,500. The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice. All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly.
The template provided in Exhibit 8-3 can be used to compute the total direct material variance, direct material quantity variance, and direct material price variance. The standard and actual amounts for direct materials quantities, prices, and totals are calculated in the top section of the direct materials variance template. All standard cost variances are calculated using the actual production quantity as the cost driver.
Supporting staff motivation initiatives and conducting suitable performance reviews are significant advantages of the process. Companies can set goals, recognize top performers, and motivate people and teams to work harder for better outcomes. This can be done by tracking and reporting variations, which helps promote overall performance and accelerates business growth. Keep in mind that there are some challenges that come with looking at specific variances. It can be a time commitment to gather records and sort through information (especially if you’re not using tools like accounting software). This shows that your actual cost was 40% greater than your prediction.
And if you’re measuring how long it took you to complete Project XYZ, you could look at the number of hours it took each department compared with your predictions. In cost accounting, a standard is a benchmark or a “norm” used in measuring performance. In many organizations, standards are set for both the cost and quantity of materials, labor, and overhead needed to produce goods or provide services. Adding the budget variance and volume variance, we get a total unfavorable variance of $1,600.
This method of overestimation, sometimes called budget slack, is built into the standards so management can still look good even if costs are higher than planned. In either case, managers potentially can help other managers and the company overall by noticing particular problem areas or by sharing knowledge that can improve variances. This method of overestimation, sometimes called budget slack, is built into the what is a business tax receipt standards so management can still look good even if costs are higher than planned. Since variable overhead is consumed at the presumed rate of $10 per hour, this means that $125,000 of variable overhead (actual hours X standard rate) was attributable to the output achieved. Comparing this figure ($125,000) to the standard cost ($102,000) reveals an unfavorable variable overhead efficiency variance of $23,000.