Variance Analysis Learn How to Calculate and Analyze Variances
Note that for some of the formulas, there are two presentations of the same formula, for example, there are two presentations of the direct materials price variance. While both arrive at the same answer, students usually prefer one formula structure over the other. The following is a summary of all direct materials variances (Figure 10.66), direct labor variances (Figure 10.67), and overhead variances (Figure 10.68) presented as both formulas and tree diagrams. Another possibility is that management may have built the favorable variance into the standards. Management may overestimate the material price, labor rate, material quantity, or labor hours per unit, for example.

Variable manufacturing overhead efficiency variance
As mentioned, it includes establishing a standard cost and calculating any differences with actual results. However, these present a single-dimensional view of variances for companies. Some companies may what is a flat rate pricing model pros and cons explained also perform other types of variance analysis to pinpoint the reasons for any variances. After that, they can calculate their actual performance and calculate any variances from the set standards.
Direct materials price variance
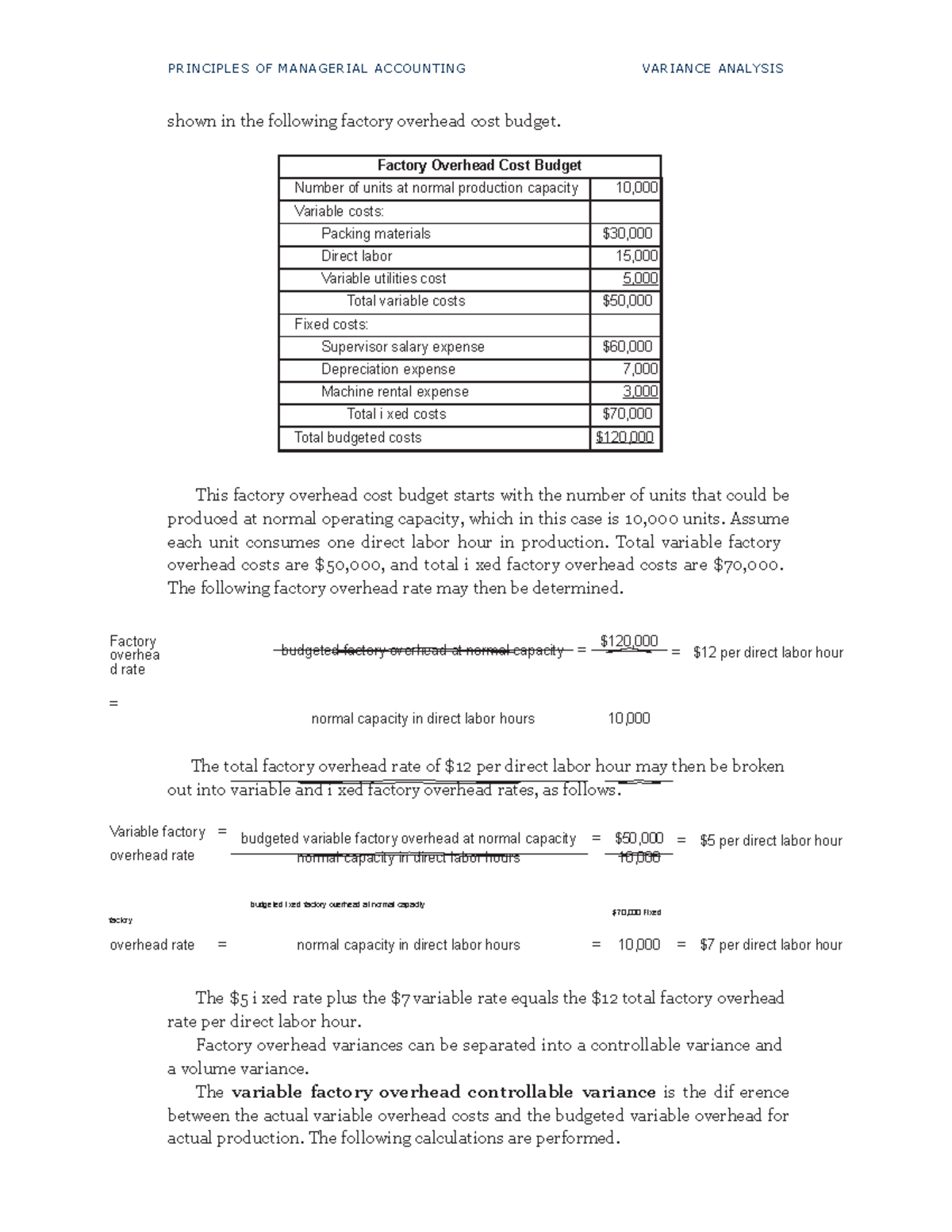
Although the product was selling well, product costs were higher than expected, translating into lower profits. Brad decided to conduct a standard costs variance analysis to see if he could isolate the issue, or issues. The standard costs to make one unit of NoTuggins and the actual production costs data for the period are presented in Exhibit 8-1 below. When calculating the fixed overhead variances in absorption costing, companies must establish a standard absorption rate. Based on that rate, companies can calculate the differences between actual and expected absorbed overheads.
9 Management’s Use of Variance Analysis
There are no specific requirements for management accounting, unlike financial accounting, which makes it different. Requiring managers to determine what caused unfavorable variances forces them to identify potential problem areas or consider if the variance was a one-time occurrence. Requiring managers to explain favorable variances allows them to assess whether the favorable variance is sustainable. Knowing what caused the favorable variance allows management to plan for it in the future, depending on whether it was a one-time variance or it will be ongoing.
- In this formula, divide what you actually spent or used by what you predicted.
- A template to compute the total variable manufacturing overhead variance, variable manufacturing overhead efficiency variance, and variable manufacturing overhead rate variance is provided in Exhibit 8-9.
- As with any variable cost, the per unit cost is constant, but the total cost depends on the quantity produced or another cost driver.
- This could occur because the company was able to hire workers at a lower rate, because of negotiated union contracts, or because of a poor labor rate estimate used in creating the standard.
- The other variance computes whether or not actual production was above or below the expected production level.
These can come from various sources, such as material or labour quality, usage efficiency, wastages, skilled labour, changes in products, incorrect budgeting, etc. Sometimes, usage variances or efficiency may be indirectly dependent on price variances. For example, cheaper materials may cause favorable price variances but may cause adverse usage variances as well.
What is Controllable Variance? Definition, Formula, Example
SQ and SP refer to the “standard” quantity and price that was anticipated. The completed top section of the template contains all the numbers needed to compute the direct labor efficiency (quantity) and direct labor rate (price) variances. The direct labor efficiency and rate variances are used to determine if the overall direct labor variance is an efficiency issue, rate issue, or both.
Lastly, they can investigate these differences to identify the reasons behind them and control them in the future. Variance analysis is a process that companies use to identify the differences between standard and actual costs. Through this process, companies study the deviations of forecasted or planned behaviour with actual results. Once they do so, they can understand the causes of any variances and control them in the future. A favorable labor rate variance occurred because the rate paid per hour was less than the rate expected to be paid (standard) per hour.
Since direct labor hours are the cost driver for variable manufacturing overhead in this example, the variance is linked to the direct labor hours worked in excess of the standard labor hours allowed. This overage in direct labor hours means that $22,500 of additional variable manufacturing overhead was incurred based on the standard amount applied per direct labor hour. Inefficient use of the cost driver used to apply variable manufacturing overhead typically results in additional overhead costs. However, variations in costs or prices and usage or efficiency only apply to variable costs or sales. It is because fixed overheads do not usually change with activity levels.